MHC - Mount Hamilton
We operate broadband and borehole stations under the network code BK. The Berkeley Digital Seismic Network (BDSN) is a regional network of very broadband and strong motion seismic stations designed to monitor regional seismic activity as well as provide high quality data. The Berkeley borehole stations have borehole geophones or other seismic sensors and may have other geophysical instrumentation.
BARD is our GPS network for monitoring crustal deformation across the Pacific-North America plate boundary and in the San Francisco Bay Area for earthquake hazard reduction studies and rapid earthquake emergency response assessment
| Station Name | MHC (MHC2) |
| In Operation | 1986/09/10 00:00:00 - Present |
| Latitude | |
| Longitude: | |
| Elevation: | 1261.8984 meters |
| Instrumentation | Broadband GPS |
Location
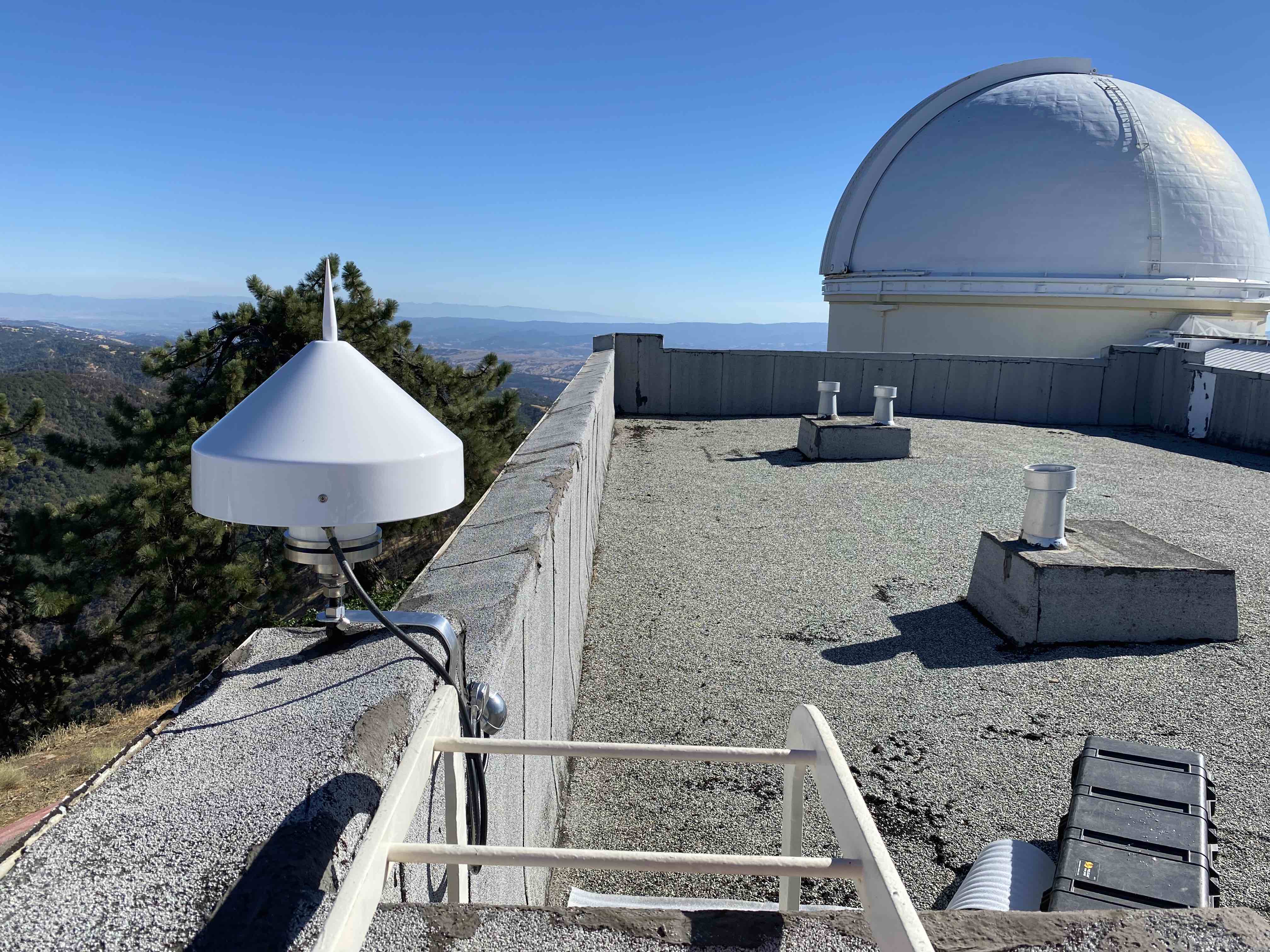
Site is located at the Lick Observatory atop Mount Hamilton, and is under the auspices of UC Santa Cruz. The site was first established in 1887 with the installation of the first seismic sensors in North America, and has been occupied continuously since then. Wood-Anderson seismographs were deployed at this site in 1928 and operated until 1993. The first digital broadband instrumentation was deployed in 1987.Network
Berkeley Digital Seismic Network (BK)Bay Area Regional Deformation Network (BARD)
Geology
Jurassic-Cretaceous Franciscan greywacke and greenstone
Borehole Conditions
The vault is located in a room in the east wing of the Lick Observatory. The piers are reinforced concrete which are isolated from the building. The seismometer room is isolated from the hallway via two doors and the datalogger and supporting equipment are in an adjacent room. The seismometers are thermally insulated with 4" of polyurethane foam.GPS Monument Description
Threaded rod cemented into roof of structure.Table of Seismic Instrumentation
| Sensor | Datalogger | SEED Channels | Location | |
| Broadband | Streckeisen STS-7 VBB Tri-Axial Seismometer | Q330HR-GFE | BH?,HH?,LH?,VH? | 00 |
| Accelerometer | EPISENSOR ES-T | Q330HR-GFE | HN? | 00 |
| Auxiliary | AntennaCurrent | Q330HR-GFE | VE? | 00 |
| ClockPhase | Q330HR-GFE | LC?,VC? | 00 | |
| ClockQuality | Q330HR-GFE | LC?,VC? | 00 | |
| InputVoltage | Q330HR-GFE | VE? | 00 | |
| SystemCurrent | Q330HR-GFE | VE? | 00 | |
| SystemTemperature | Q330HR-GFE | VK? | 00 | |
| VCOValue | Q330HR-GFE | VC? | 00 |
GPS Instrumentation
| Receiver | Antenna | Radome | - | |
| GPS | SEPTENTRIO POLARX5 | SEPTENTRIO SEPCHOKE_B3E6 | SPKE | - |
Waveforms and associated metadata, and GPS data, are available at the Northern California Earthquake Data Center (NCEDC).
Waveform Data
- BK Information Directory, including
- List of station locations
- List of available channels
- Instrument Response
- Querying the archives
- Download waveform data
GPS Data
- Site log: mhc2.log
Data Type From To Low-rate raw 08/12/2022 present Low-rate rinex 08/12/2022 present High-rate raw 08/12/2022 present High-rate rinex 08/12/2022 present
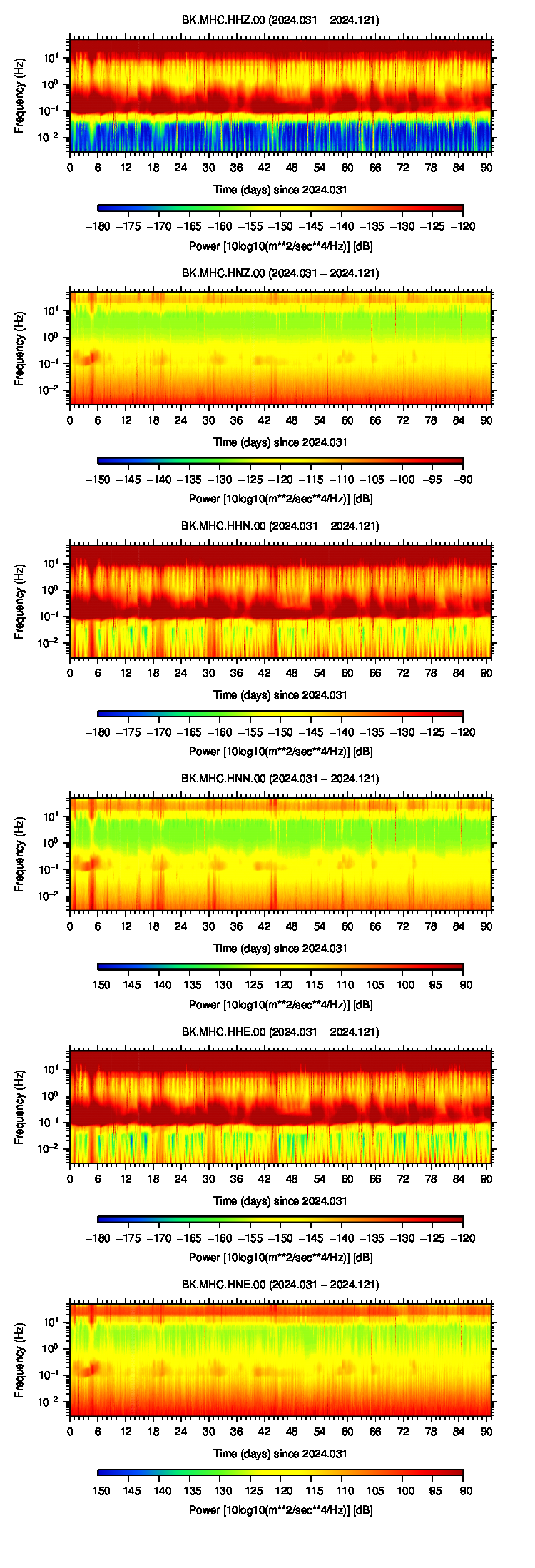
Noise Analysis
 |
GPS Data Quality
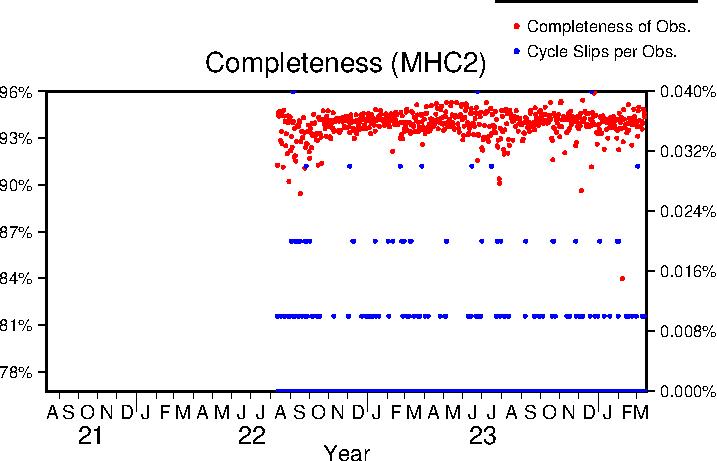
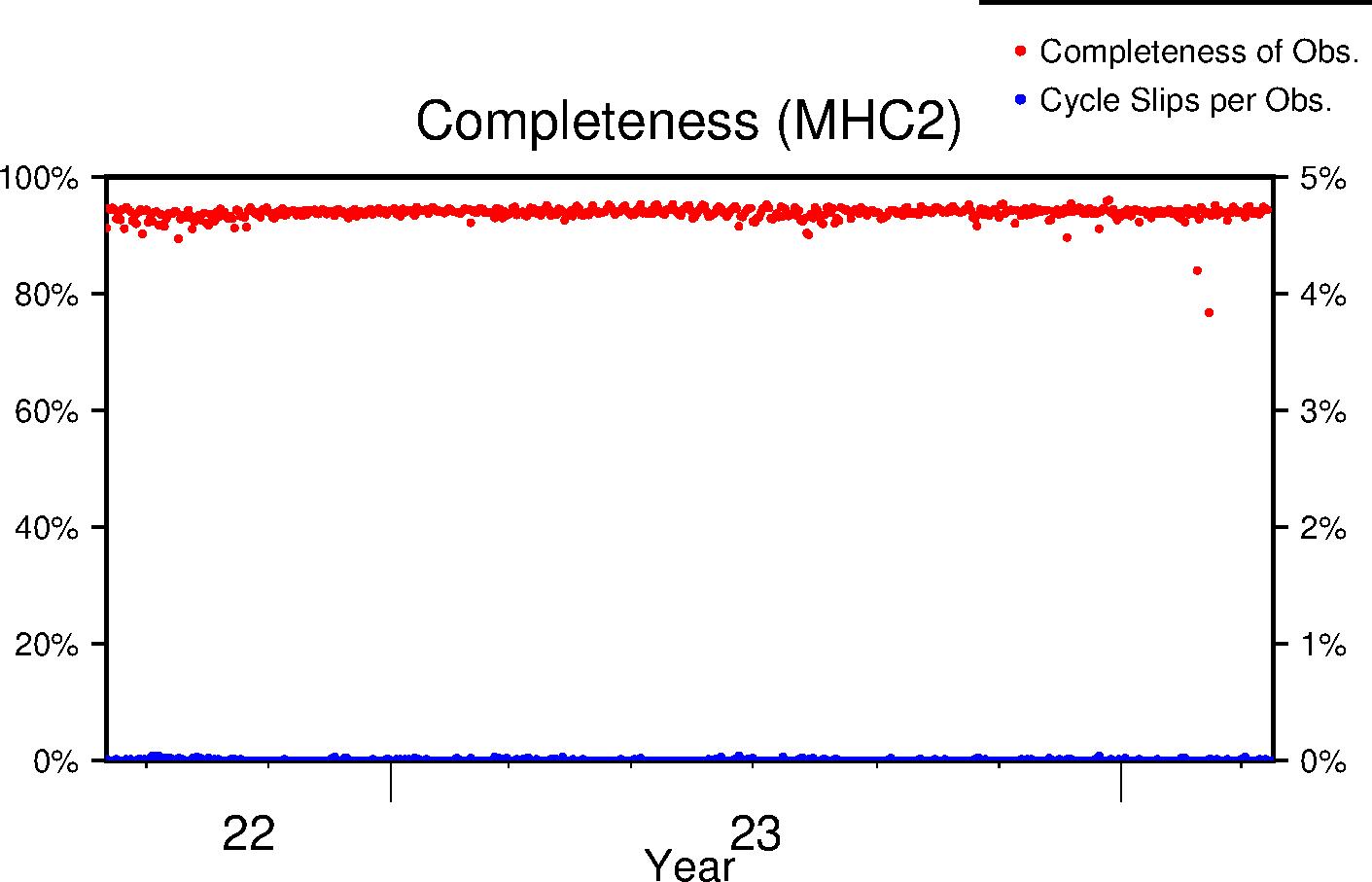
Completeness
Data completeness is defined both as "Completeness of observations" and "Cycle slips per observation". "Completeness of Obs." is the number of epochs in the final RINEX file normalized to the expected number. This percentage will go down if time is missing from the RINEX file. "Cycle slips per Obs." is the total number of detected cycle slip normalized to the total number of observations in the RINEX file. This number will increase as the receiver loses lock on satellites more frequently.
| Previous Year |
 |
| Lifetime |
 |
Multipath
The effects of multipath on the data are estimated by parameters for L1 and L2 (MP1 and MP2 respectively); see Estey and Meertens (GPS Solutions, 1999) for derivation. The daily value is the RMS of MP1 and MP2 throughout the day and for all satellites. Higher values indicate a greater prevalence and/or strength of multipathing, i.e. objects on the ground are providing multiple reflection pathways from the satellite to antenna.
| Previous Year |
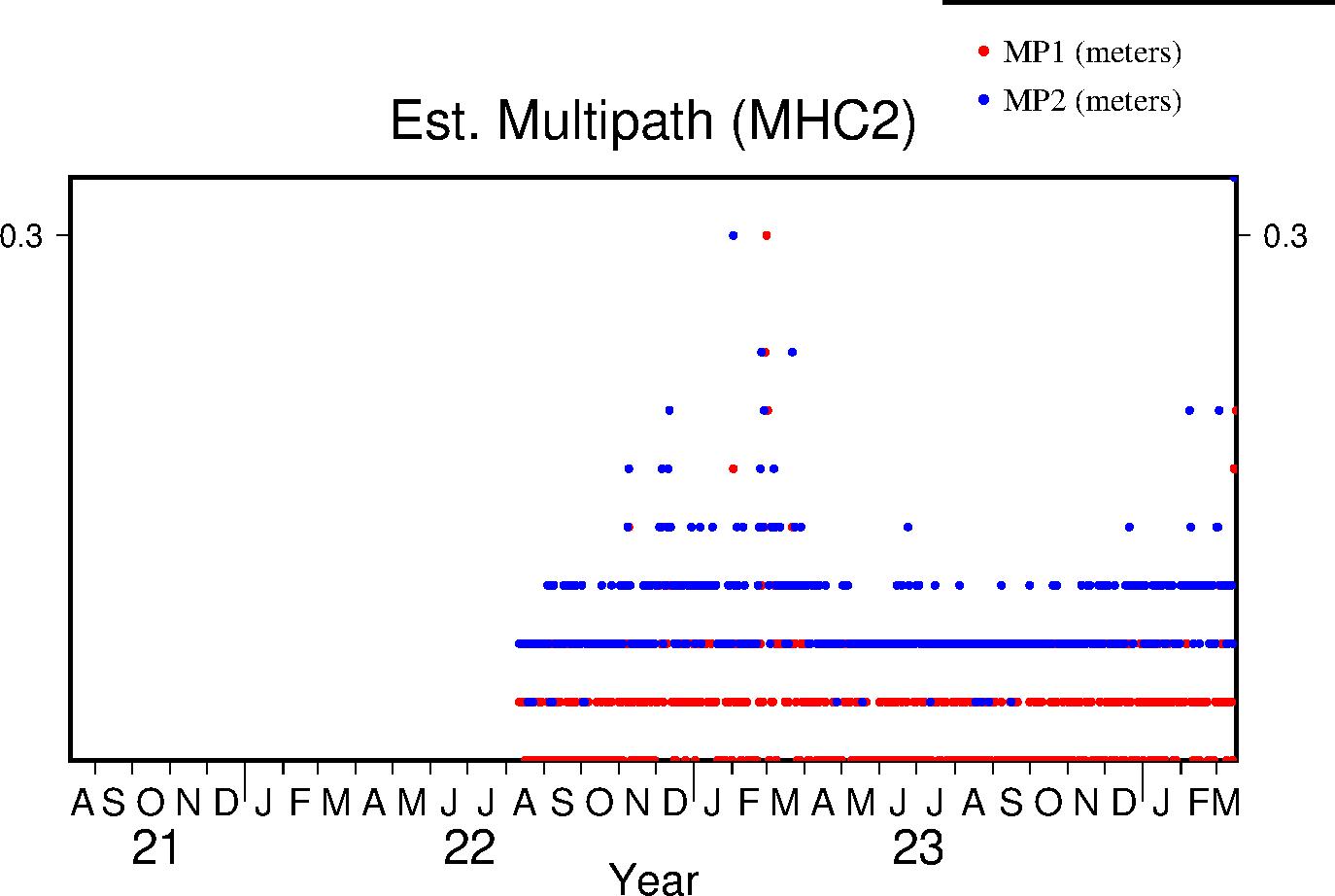 |
| Lifetime |
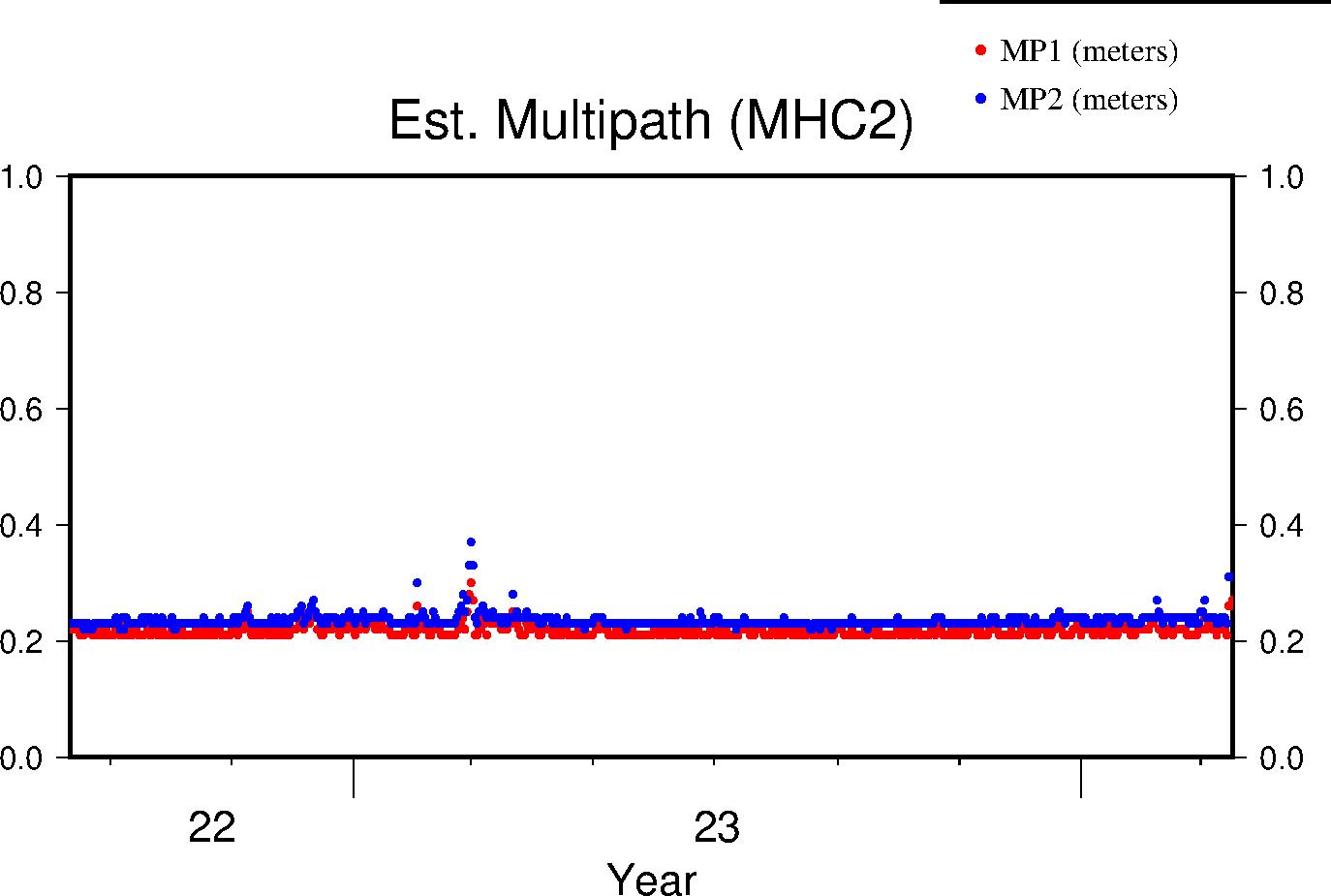 |
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
The Signal-to-Noise ratios are the mean values above the QC elevation mask for L1 and L2 respectively.
| Previous Year |
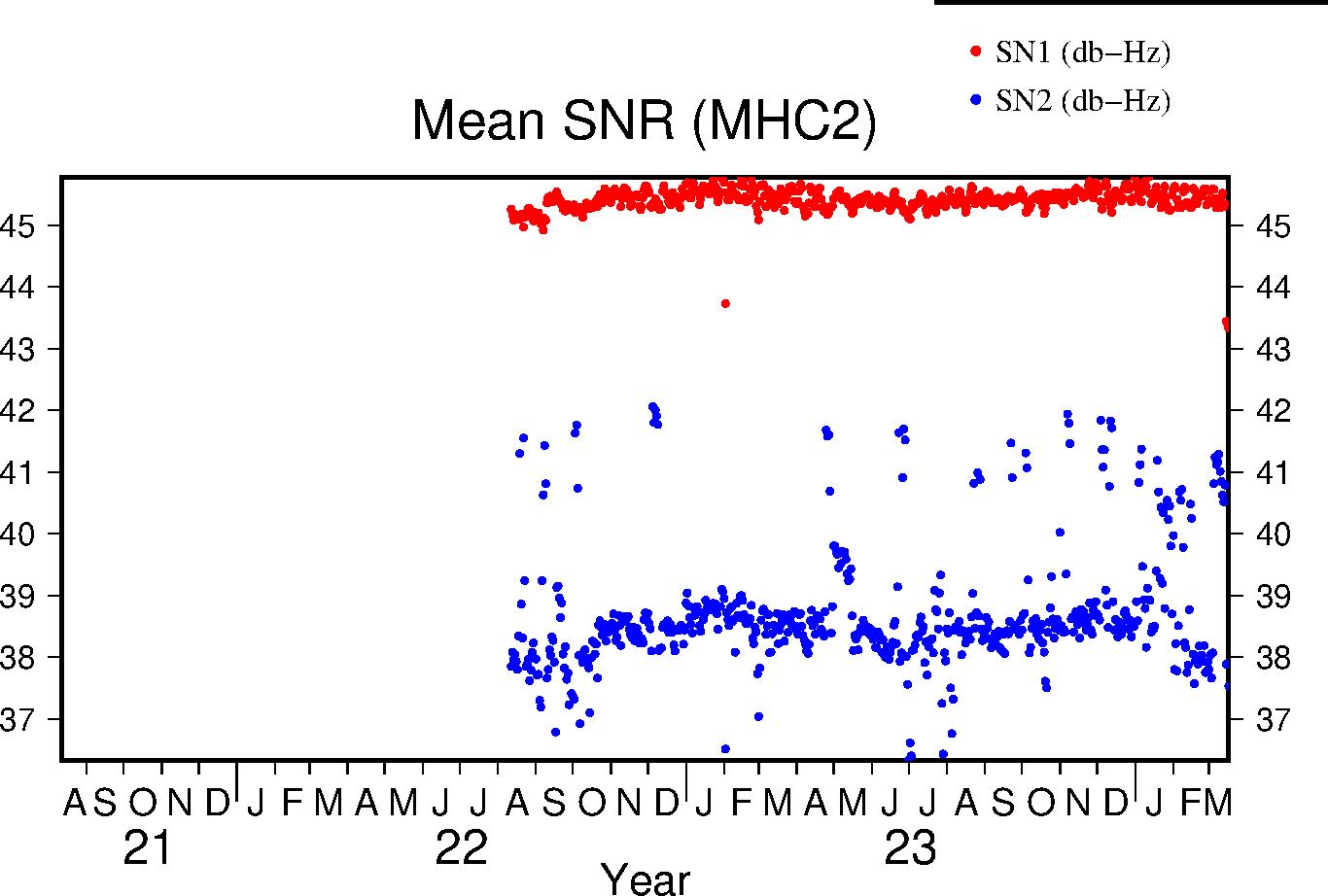 |
| Lifetime |
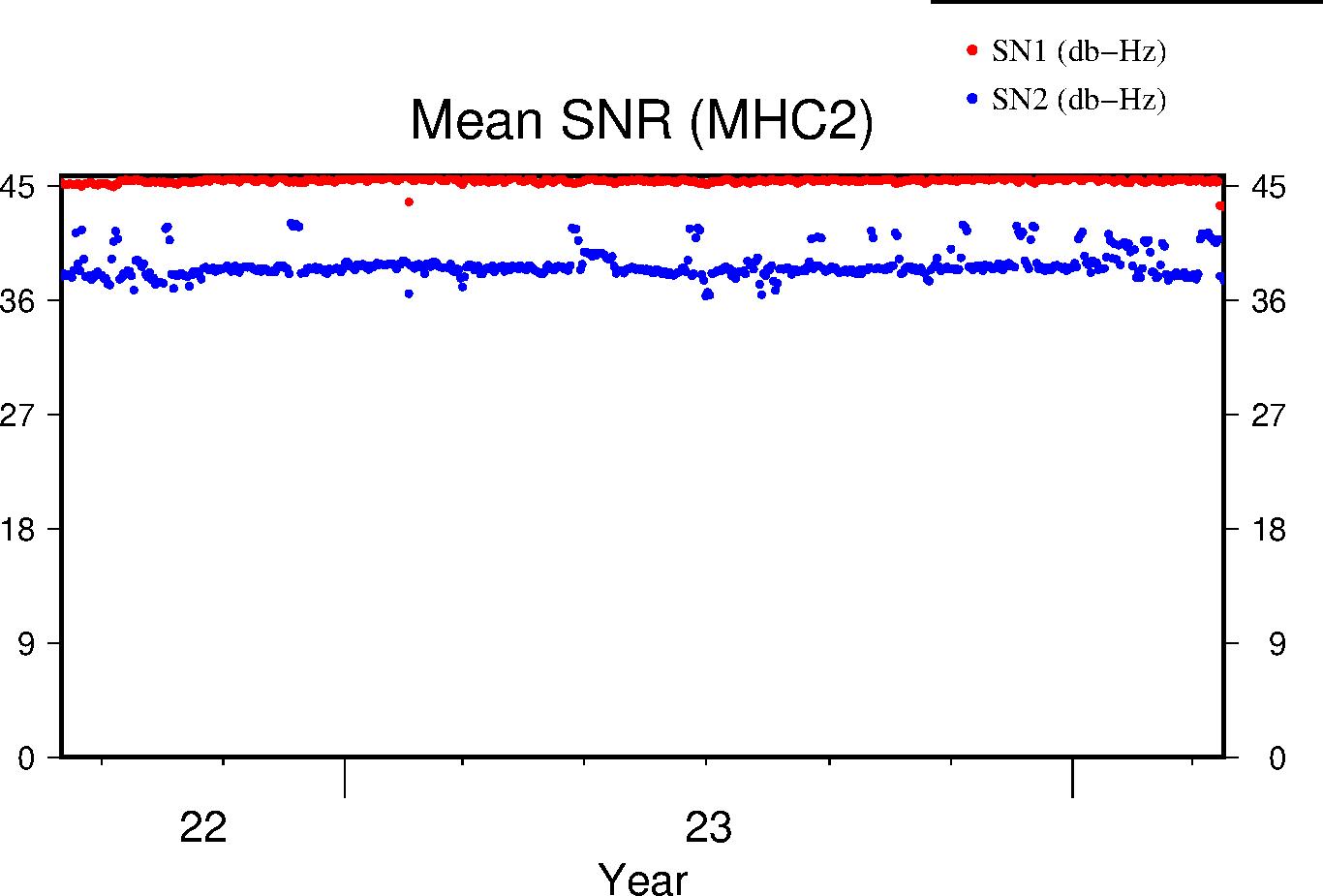 |